This is in accordance with the matching principle of accounting, which dictates that expenses should be matched with the revenues they help to generate in the same period. If no direct connection to revenue can be established, the costs are recognized in the period they arise. For instance, office rent is recorded as an expense in the month it is paid, irrespective of the sales activities of that month. This treatment ensures that the financial statements accurately reflect the company’s operational costs and help in assessing its profitability during a specific accounting period.
How do you calculate operating costs?
Product costs only become an expense when the products to which they are attached are sold. Period expenses are important to know about because they can have a direct impact on both reducing costs and increasing revenue. However, if these costs become excessive they can add significantly to total expenses and they should be monitored closely so managers can take action to reduce them when possible. These costs include items that are not related directly to the primary function of a business, such as paying utility bills or filing legal suits.
Calculate Total Period Cost

By learning the intricacies of total period cost calculation, companies can identify potential areas for cost reduction and enhance their profitability. Additionally, the formulation assists in streamlining processes by period costs formula aligning expenses with the company’s financial objectives. Effective calculation influences not only internal assessments and improvements but also affects how investments and pricing strategies are planned. As a non-cash expense, depreciation appears on the income statement but does not directly drain cash flow.
How does the accounting term “period expense” differ from an operating expense?
Period costs are not tied to a product or the cost of inventory like product costs are. Period costs are also listed as an expense in the accounting period in which they occur. Some examples of what a product costs include, direct labor, raw materials, manufacturing supplies, and overhead that is directly tied to the production facility, such as electricity. To calculate total period costs, management accountants identify all expenses that qualify as period costs for the specific reporting period and sum them up. This includes selling expenses, administrative expenses, and any other costs considered not directly related to production.
- This means that 20% of the company’s revenue remains as profit after deducting all expenses, indicating greater profitability.
- However, these costs are still paid every period, and so are booked as period costs.
- Period expenses appear on the income statement with an appropriate caption for the item, which acts as a disclosure, in the period when the cost is incurred or recognized.
- Understanding and managing operating costs is an important part of running a business.
- Understanding these costs is not just about recording numbers; it’s about grasping their broader implications on pricing strategies, budgeting, forecasting, and tax considerations.
- This calculation helps in understanding the financial efficiency of operational practices over the period.
Period Cost vs Product Expense
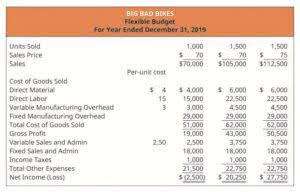
Period costs are only reported on the income statement for the period in which they are used up or incurred. So, it is only for that accounting period that period costs will reduce the net income. Additionally, businesses must be agile in their pricing strategies to respond to fluctuations in period costs. For instance, a spike in rental expenses due to market changes would necessitate a reevaluation of pricing to ensure that the increased costs do not erode profit margins. This agility helps businesses remain competitive and financially healthy in a dynamic economic environment.
Find the talent you need to grow your business
Examples of product costs include the cost of raw materials used, depreciation on plant, expired insurance on plant, production supervisor salaries, manufacturing supplies used, and plant maintenance. Understanding and managing operating costs is an important part of running a business. If you don’t track and try to reduce your operating costs when needed, your profit margin may suffer. Easy-to-use accounting software like QuickBooks Online makes these costs apparent and helps you eliminate unnecessary expenses.

Understanding Period Costs
These ratios can be compared to industry averages gross vs net or competitors to assess a company’s relative efficiency and profitability. This means that 20% of the company’s revenue remains as profit after deducting all expenses, indicating greater profitability. Operating costs are the costs of maintaining the day-to-day operations of your business, such as rent, cost of goods sold (COGS), and payroll. Accounting for both types of expenses is key for profitable pricing strategies.
Real-world example of operating costs
These costs are expensed immediately on the income statement rather than being included in the costs of goods sold. In this post, you’ll learn the key differences between period and product costs along with real-world examples to clearly illustrate the implications of proper classification. Most business owners would agree that properly classifying costs as either “period” or “product” expenses is critical for accurate financial reporting and strategic decision making. Overhead, or the costs to keep the lights on, so to speak, such as utility bills, insurance, and rent, are not directly related to production.
Knowing how operating costs are depicted on each statement is essential for understanding Bookkeeping for Veterinarians a company’s financial performance and making informed business decisions. Operating expenses include all of the above except the interest and tax expenses. So, for the manufacturer, the operating costs are $190,000, which is COGS of $75,000 plus the total operating expense of $115,000. These are the ongoing costs of running your business, such as rent, salaries, utilities, and marketing.


