To further illustrate the analysis of transactions and their effects on the basic accounting equation, we will analyze the activities of Metro Courier, Inc., a fictitious corporation. Refer to the chart of accounts illustrated in the previous section. As we’ve learned previously, the accounting equation is a mathematical expression that shows the relationship among the different elements of accounting, i.e. assets, liabilities, and capital (or “equity”). Capital essentially represents how much the owners have invested into the business along with any accumulated retained profits or losses. The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner.
What Is a Liability in the Accounting Equation?
An asset is a resource that is owned or controlled by the company to be used for future benefits. Some assets are tangible like cash while others are theoretical or intangible like goodwill or copyrights. These are some simple examples, but even the most complicated transactions can be recorded in a similar way. This equation is behind debits, credits, and journal entries. Metro Corporation collected a total of $5,000 on account from clients who owned money for services previously billed.
Assets, Liabilities, And Equity
Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners. If a transaction is completely omitted from the accounting books, it will not unbalance the accounting equation. After the company formation, Speakers, Inc. needs to buy some equipment for installing speakers, so it purchases $20,000 of installation equipment from a manufacturer for cash. In this case, Speakers, Inc. uses its cash to buy another asset, so the asset account is decreased from the disbursement of cash and increased by the addition of installation equipment.
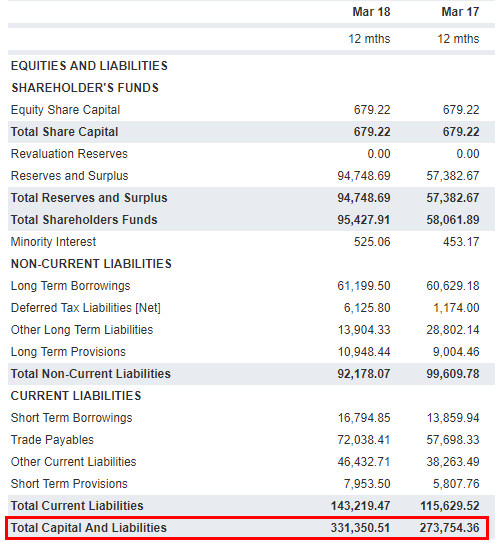
4: The Basic Accounting Equation
- Notice that every transaction results in an equal effect to assets and liabilities plus capital.
- To learn more about the income statement, see Income Statement Outline.
- All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
- The total dollar amounts of two sides of accounting equation are always equal because they represent two different views of the same thing.
As transactions occur within a business, the amounts of assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity change. As business transactions take place, the values of the accounting elements change. The accounting equation nonetheless always stays in balance. Knowing how to calculate retained earnings helps business owners to perform a more in-depth financial analysis.

The accounting equation plays a significant role as the foundation of the double-entry bookkeeping system. The primary aim of the double-entry system is to keep track of debits and credits and ensure that the sum of these always matches up to the company assets, a calculation carried out by the accounting equation. It is based on the idea that each transaction has an equal effect.
Net income equation
Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It can be found on a balance sheet and is one of the most important metrics for analysts to assess the financial health of a company. When the total assets of a business increase, then its total liabilities or owner’s equity also increase.
The cost of this sale will be the cost of the 10 units of inventory sold which is $250 (10 units x $25). The difference between the $400 income and $250 cost of sales represents a profit of $150. The inventory (asset) will decrease by $250 and apps for accountants a cost of sale (expense) will be recorded. (Note that, as above, the adjustment to the inventory and cost of sales figures may be made at the year-end through an adjustment to the closing stock but has been illustrated below for completeness).
Accounting equation describes that the total value of assets of a business entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner’s equity. This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used by small proprietors to large multinational corporations. Other names used for this equation are balance sheet equation and fundamental or basic accounting equation. The accounting equation is the backbone of the accounting and reporting system. It is central to understanding a key financial statement known as the balance sheet (sometimes called the statement of financial position).
As you can see, no matter what the transaction is, the accounting equation will always balance because each transaction has a dual aspect. The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions. Our Explanation of Accounting Equation (or bookkeeping equation) illustrates how the double-entry system keeps the accounting equation in balance.


